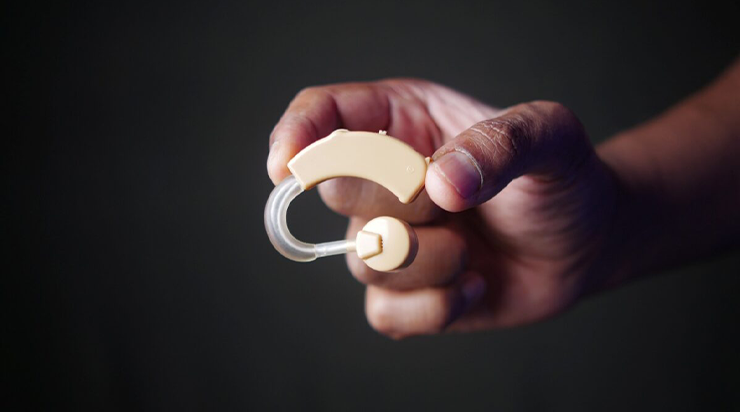
Cross-sector collaboration is redefining how assistive technologies are funded, developed, and distributed. We explore some powerful public-private partnership (PPP) models in India.
Regional Chapters by 2026
International Partners by 2027
Startups Supported by 2028
Govt Projects Targeted by 2026
CSR and Innovation Grants
India’s CSR law mandates 2% profits for social causes, and assistive technology is increasingly eligible. Large corporates are sponsoring R&D labs, hackathons, and rehab centers. Infosys Foundation, HCL, and Tata Trusts are notable contributors.
Government schemes like Startup India Seed Fund and BIRAC’s Biotech Ignition Grant also prioritize AT startups. PPP models allow quicker piloting, validation, and last-mile delivery of new tech.
Distribution & Inclusion Models
Innovative collaborations between hospitals, NGOs, and governments are helping AT products reach underserved populations. Some states use PPPs to distribute smart devices in rural schools and public clinics.
AATMA has a role in standardizing partnership frameworks, maintaining quality oversight, and helping members co-develop proposals. The goal is to create repeatable, scalable models.

Summary
- CSR funds powering AT innovation.
- BIRAC and Startup India grants active.
- PPP for rural AT distribution.
- Role of NGOs and local govts.
- Standardized PPP models needed.
- AATMA can connect stakeholders.